Fibre Optics (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
Fibre Optics
Total internal reflection is used to reflect light along optical fibres
Light, that is normally monochromatic, refracts when it enters the optical fibre at one end
It undergoes repeated total internal reflection against the sides of the fibre until it reaches the other end
Where it is refracted back out
In this process, the light signals travel long distances without losing information or speed
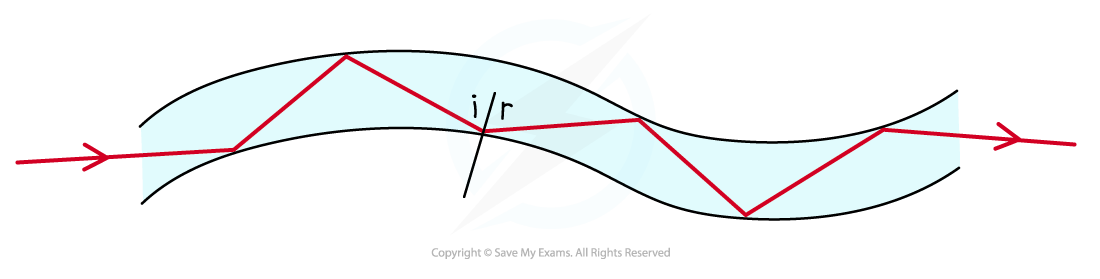
Optical fibres utilise total internal reflection where the angle of incidence on the side of the fibre is greater than the critical angle
These have many important uses, including:
Communications, such as telephone and internet transmission
Medical imaging, such as endoscopes
The three main components of optical fibres are:
An optically dense core tube, made of plastic or glass
A lower optically dense cladding surrounding the core
An outer sheath

A light ray is totally internally reflected down an optical fibre against the core-cladding boundary
TIR only occurs when ncladding < ncore
This type of optical fibre is called a step-index fibre because the refractive index of each component increases moving from the outside to the centre of the fibre
The role of the cladding is to:
Protect the thin core from damage and scratching
Prevent signal degradation through light escaping the core, which can cause information from the signal to be lost
It keeps the signals secure and maintains the original signal quality
It keeps the core separate from other fibres preventing information crossover
Material & Modal Dispersion
Material and model dispersion both cause pulse broadening
Where the pulses emerging from the fibre are longer than those entering
Material Dispersion
When white light is used instead of monochromatic light inside an optical fibre it is separated into all the colours of the spectrum
The white light is therefore dispersed, so the beam gets wider as it travels down the optical fibre

White light is dispersed into its spectral components
Each wavelength of light travels at the same speed in a vacuum but at different speeds in a medium
Violet light has the shortest wavelength, so it travels the slowest in the fibre
This means its angle of incidence on the fibre boundary is smallest compared to the other colours
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, so the angle of reflection is also smaller
This means it takes longer for the violet colour to travel down the fibre because it undergoes more reflections

Remember when a light ray is reflected then the angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Modal Dispersion
Modal dispersion occurs when the monochromatic light pulses in the optical fibre spread out
This is because each part of the wavefront has a different angle of incidence and consequently a different angle of reflection
So each part of the wavefront undergoes total internal reflection a different number of times
Hence, each part of the wavefront reaches the end of the fibre at a slightly different time
This effect is more prominent when the core of the fibre is wider
So the total internal reflection takes place more times
To prevent modal dispersion, the core needs to be very narrow

Modal dispersion occurs in a wide optical fibre where it spreads out and broadens
Pulse Broadening & Absorption
The absorption of a signal in an optical fibre occurs when the fibre absorbs part of the signal’s energy
This reduces the amplitude of the signal, which can lead to a loss in the information transmitted
Pulse broadening is caused by modal and material dispersion
This can result in the merging of pulses, which distorts the information in the final pulse and decreases the amplitude of the signal

Reducing Pulse Broadening & Absorption
To reduce absorption:
Use an extremely transparent core
Use optical fibre repeaters so the pulse is regenerated before significant absorption has taken place
To reduce pulse broadening:
Use a core that is as narrow as possible to reduce the possible differences in the path length of the signal
Use of a monochromatic source so the speed of the pulse is constant
Use optical fibre repeaters so the pulse is regenerated before significant pulse broadening has taken place
Use a single-mode fibre, where only a single wavelength of light passes through the core, to reduce multipath modal dispersion
Worked Example
A cross-sectional view of a step-index optical fibre is shown in the diagram.

The light ray enters the end of the fibre and refracts along the core-cladding boundary.
Calculate the angle of incidence, θ, of the ray at the point of entry to the fibre.
The speed of light in the core is 2.027 × 108 m s–1
The speed of light in the cladding is 2.055 × 108 m s–1
Answer:





Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
