Quick Sort (OCR A Level Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: H446
Quick sort
What is a quick sort?
A quick sort is another example of a divide and conquer algorithm that reduces the size of the problem into smaller problems that are more easily solvable by an algorithm
Below is an illustration of the quick sort

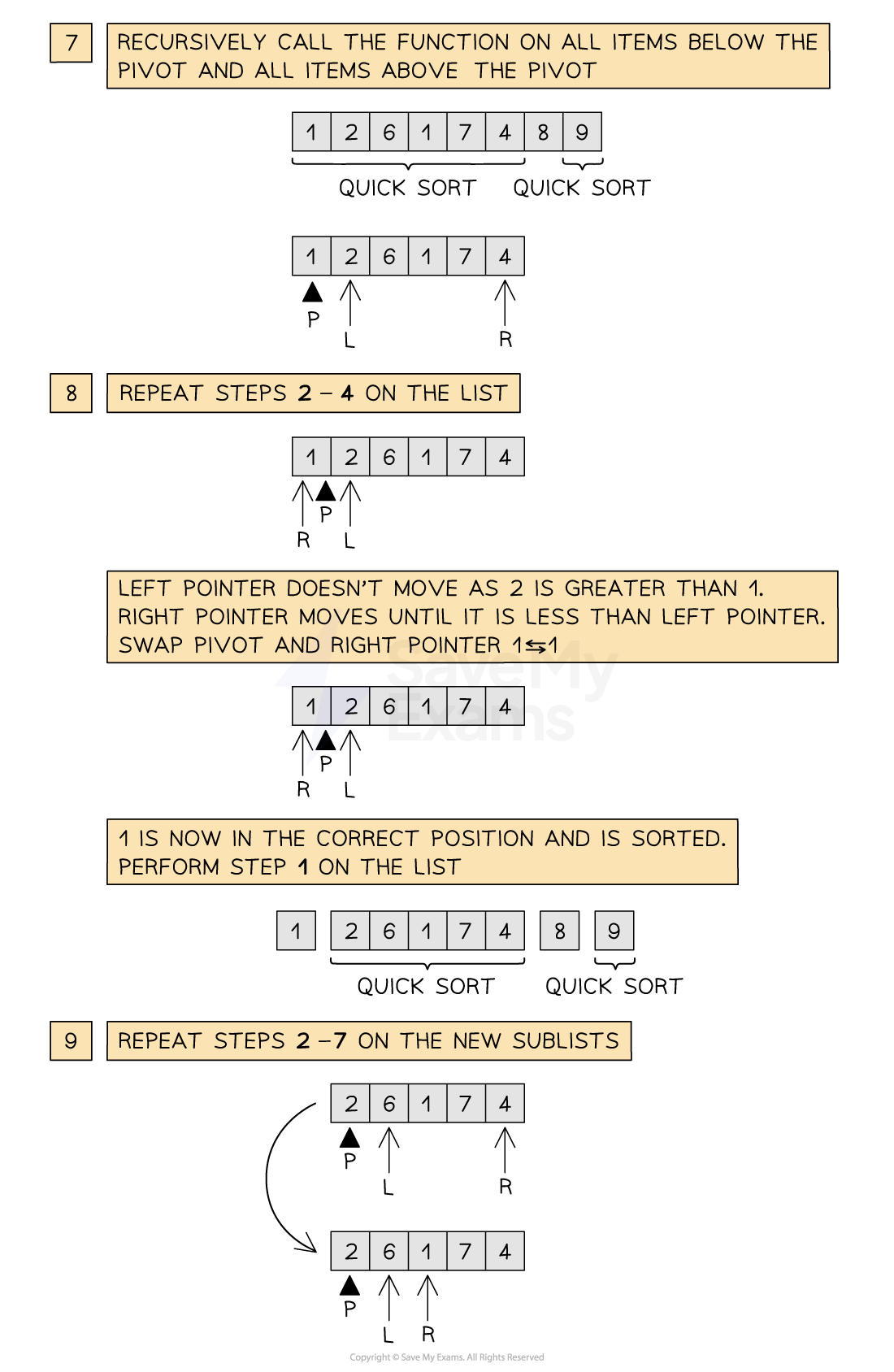
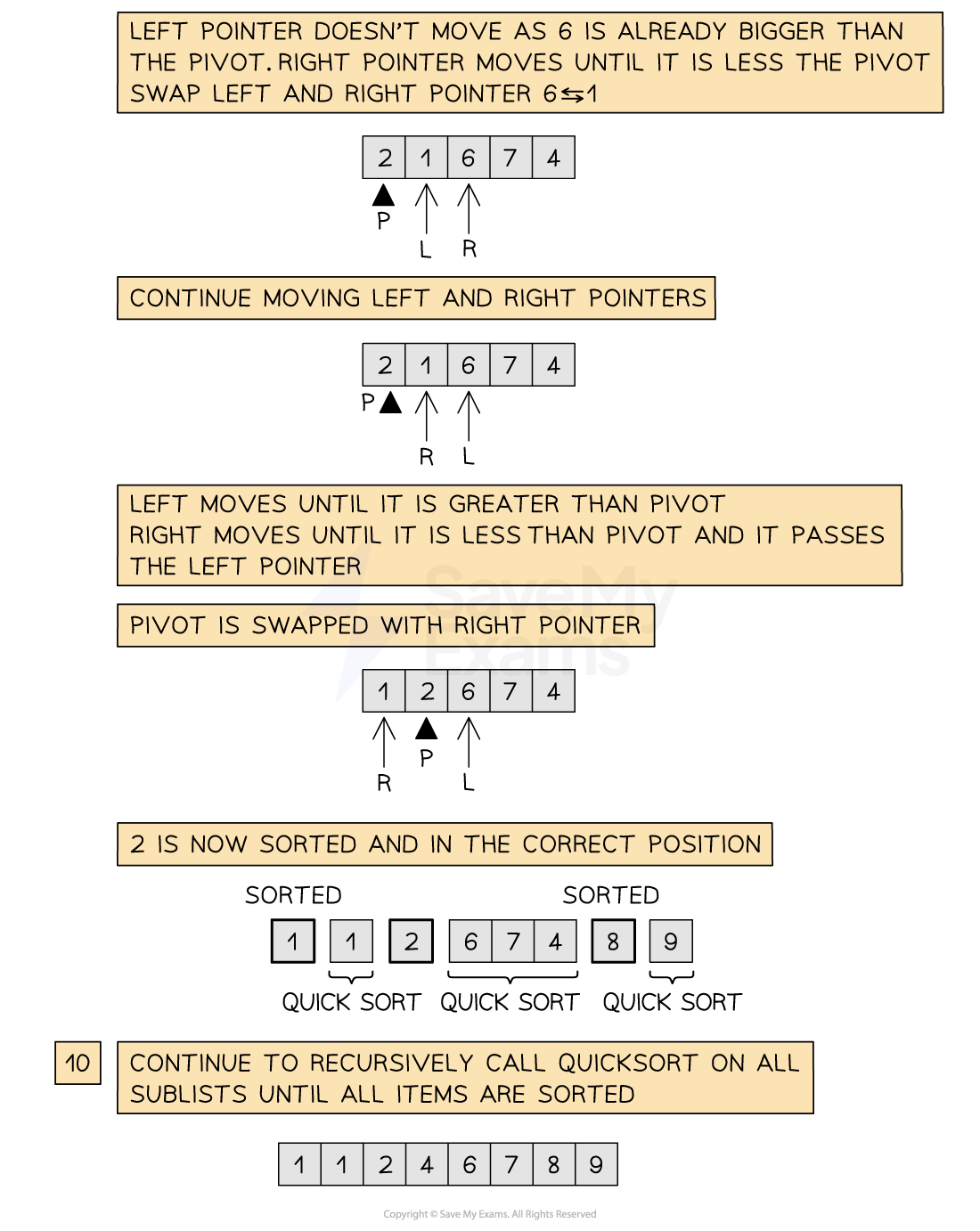
Figure 2: Performing the Quick sort
Time complexity of quick sort
Quick sort is a divide and conquer algorithm that splits the problem into smaller subproblems using a pivot value
The pivot divides the list into two parts: values less than the pivot and values greater than the pivot
Each sub list is then sorted recursively until the list is completely ordered
Best and average case
If the pivot divides the list roughly in the middle, the algorithm performs efficiently
Each level of recursion performs n operations to partition the list
There are approximately log n levels of recursion
This gives a best and average case time complexity of O(n log n)
Worst case
If the pivot is consistently placed at one extreme (for example, always the smallest or largest value), one partition becomes empty
This causes the recursion to degenerate into a single chain of calls
Each recursive call processes n – 1 elements, leading to n × (n – 1) operations, or O(n²) overall
Poor pivot selection or already sorted input data can lead to this worst-case scenario
In practice, randomised or median-of-three pivot selection is used to avoid the worst case
If recursion depth becomes too large, a stack overflow can occur due to too many recursive calls
Space complexity of a quick sort
Quick sort requires additional memory as copies of lists are made and put on the stack. The overall space complexity is therefore O(n) with O(n) additional space required
Tracing a quick sort
The trace table below shows the process of calling the quick sort and moving the left and right pointers up and down the list to find elements to swap and then find the correct position of the pivot
Once the pivot is in place, quick sort is recursively called on both sublists on either side of the pivot. Note that a second call to quick sort may not exist if the pivot value ends on either extreme of the list
The process repeats, calling quick sort on progressively smaller sublists until all values are in the correct order
Trace Table for the Quick sort
list | operation | done | pivot | list[pivot] | left | list[left] | right | list[right] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[8, 2, 6, 1, 7, 9, 1, 4] | QUICKSORT | False | 0 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 4 |
| INC LEFT |
|
|
| 1 | 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 | 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 4 | 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 5 | 9 |
|
|
| DEC RIGHT |
|
|
|
|
| 7 | 4 |
[8, 2, 6, 1, 7, 4, 1, 9] | SWAP |
|
|
| 5 | 4 | 7 | 9 |
| INC LEFT |
|
|
| 6 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7 | 9 |
|
|
| DEC RIGHT |
|
|
|
|
| 6 | 1 |
[1, 2, 6, 1, 7, 4, 8, 9] | SWAP PIVOT | True | 6 | 8 | 7 | 9 | 0 | 1 |
[1, 2, 6, 1, 7, 4] | QUICKSORT | False | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| INC LEFT |
|
|
| 1 | 2 |
|
|
| DEC RIGHT |
|
|
|
|
| 5 | 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 4 | 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 | 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 | 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 1 |
| SWAP PIVOT | True | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
[2, 6, 1, 7, 4] | QUICK SORT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONTINUE UNTIL ALL ITEMS SWAPPED | ||||||||
[1, 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Worked Example
A 1-dimensional array stores a set of numbered cards from 0 to 7. An example of this data is shown below
[2, 0, 1, 7, 4, 3, 5, 6]
A programmer is writing a computer program to sort the cards into the correct order (0 to 7).
i) Show how an insertion sort would sort the array in above into the correct order. Draw the array after each move
3 marks
ii) Describe how a quick sort algorithm works with the data in shown above.
6 marks
i)
[2, 0, 1, 7, 4, 3, 5, 6]
[0, 1, 2, 7, 4, 3, 5, 6] [1]
Sort the 0 into place
[0, 1, 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 5, 6] [1]
Sort 4 and 3 into place
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 5, 6]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] [1]
Sort 5 and 6 into place
ii) Quick sort uses divide and conquer to split the list into sublists [1]. The first item becomes the pivot, so 2 is the pivot here [1]. Compare each item to the pivot, 0 to 2, 1 to 2, etc [1]. Two lists are created, one with items less than the pivot [0, 1] [1] and one with items more than the pivot [7, 4, 3, 5, 6] [1]. Quick sort is called on the new sublists and the lists are eventually recombined. [1]
Implementing a Quick Sort
Pseudocode
function quicksort(list, start, end)
if start <= end then
return
else
pivot = list[start]
left = start + 1
right = end
done = False
while done == False
while left <= right and list[left] <= pivot
left = left + 1
endwhile
while right >= left and list[right] >= pivot
right = right - 1
endwhile
if left < right then
temp = list[left]
list[left] = list[right]
list[right] = temp
else
done = True
endif
endwhile
temp = list[start]
list[start] = list[right]
list[right] = temp
quicksort(list, start, right - 1)
quicksort(list, right + 1, end)
endif
return list
endfunctionThe quick sort works in several stages
1) The pivot is set to the 0th element, the left pointer is set to the 1st element and the right pointer is set to the end of the list
2) The left pointer increments while it is less than or equal to the right pointer and the value indexed by the left pointer is less than or equal to the pivot value. Once the left pointer finds a value bigger than the pivot, or it passes the right pointer it stops
3) After the left pointer has been incremented, the right pointer is decremented. While the right pointer is greater than or equal to the left pointer and the value indexed by the right pointer is greater than or equal to the pivot value, the right pointer is decremented
4) If both pointers have not yet passed each other but both have finished moving, the values indexed by both pointers are swapped. The pointers then continue moving as per step 2 and 3
5) If both pointers pass each other then the swapping is done. The pivot value is then swapped with the value indexed by the right pointer. The pivot value is now in the correct position and is sorted
6) Both sides of the pivot value now exist as two new sublists. Quicksort is recursively called on both sublists and the process repeats as per step 1
7) Steps 1-7 repeat until all sublists have been sorted
Python
def quicksort(data, start, end): if start <= end: pivot = data[start] left = start + 1 right = end done = False while not done: while left <= right and data[left] <= pivot: left += 1 while right >= left and data[right] >= pivot: right -= 1 if left < right: temp = data[left] data[left] = data[right] data[right] = temp else: done = True temp = data[start] data[start] = data[right] data[right] = temp quicksort(data, start, right - 1) quicksort(data, right + 1, end) return data
data = [5, 2, 7, 4, 9, 10, 1, 8, 3]quicksort(data, 0, len(data) - 1)print(data) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10]
Java
public class QuickSort {
public static void quickSort(int[] data, int start, int end) { if (start < end) { int pivotIndex = partition(data, start, end); quickSort(data, start, pivotIndex - 1); quickSort(data, pivotIndex + 1, end); } }
private static int partition(int[] data, int start, int end) { int pivot = data[start]; int left = start + 1; int right = end; while (true) { while (left <= right && data[left] <= pivot) { left++; } while (right >= left && data[right] >= pivot) { right--; } if (left < right) { swap(data, left, right); } else { break; } } swap(data, start, right); return right; }
private static void swap(int[] data, int i, int j) { int temp = data[i]; data[i] = data[j]; data[j] = temp; }
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] data = {5, 2, 7, 4, 9, 10, 1, 8, 3}; quickSort(data, 0, data.length - 1); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data)); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10] }}

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
