Pearson's Product-Moment Correlation Coefficient (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
PMCC
What is Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient?
Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient (PMCC) is a way of giving a numerical value to the linear relationship of bivariate data
The PMCC of a sample is denoted by the letter
r can take any value in the interval
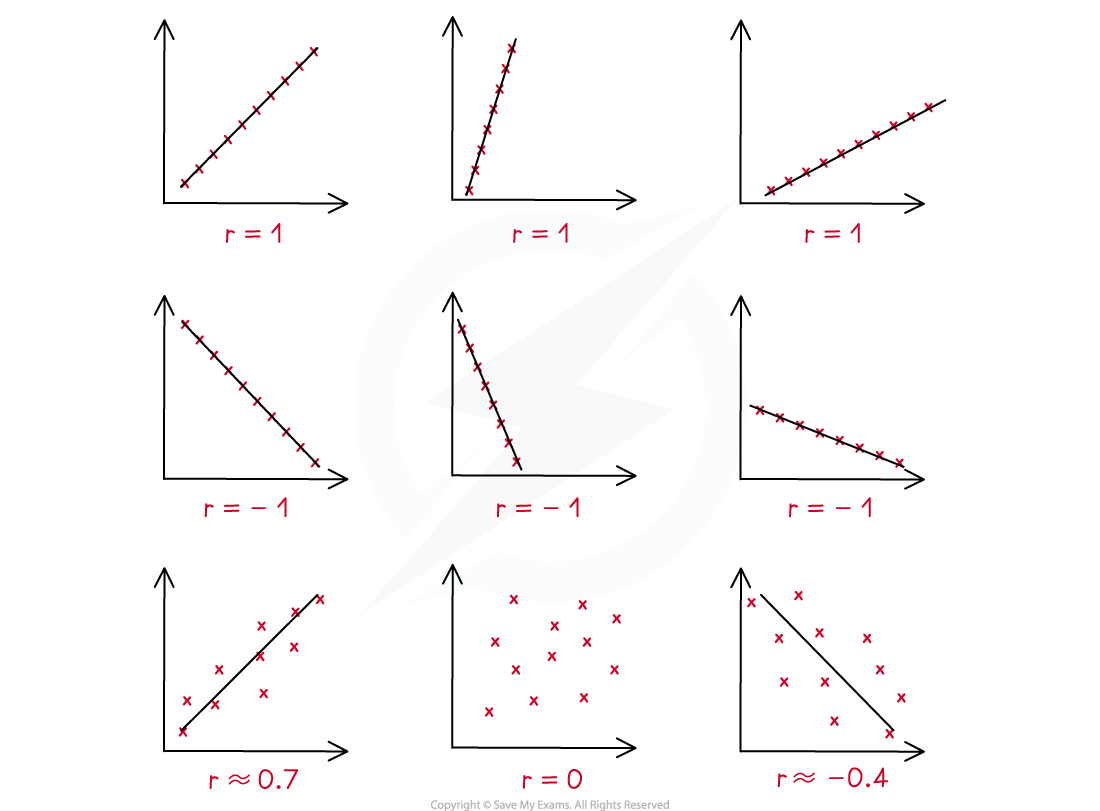
A positive value of r describes positive correlation
A negative value of r describes negative correlation
r = 0 means there is no linear correlation
r = 1 means perfect positive linear correlation
r = -1 means perfect negative linear correlation
The closer to 1 or -1 the stronger the correlation
How do I calculate Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient (PMCC)?
You will be expected to use the statistics mode on your GDC to calculate the PMCC
The formula can be useful to deepen your understanding
is linked to a statistical measure known as covariance
and
are linked to the variances
You do not need to learn this as using your GDC will be expected
When does the PMCC suggest there is a linear relationship?
Critical values of r indicate when the PMCC would suggest there is a linear relationship
In your exam you will be given critical values where appropriate
Critical values will depend on the size of the sample
If the absolute value of the PMCC is bigger than the critical value then this suggests a linear model is appropriate
Worked Example
The table below shows the scores of eight students for a maths test and an English test.
Maths | 7 | 18 | 37 | 52 | 61 | 68 | 75 | 82 |
English | 5 | 3 | 9 | 12 | 17 | 41 | 49 | 97 |
a) Write down the value of Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficient, .

b) Comment on the value of the correlation coefficients


Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?