Fusion Reactions in Stars (DP IB Physics): Revision Note
Written by: Katie M
Updated on
Fusion Reactions in Stars
Nuclear fusion is defined as:
The joining of two small nuclei to produce a larger nucleus
Low-mass nuclei, such as hydrogen and helium, can undergo fusion and release energy
For example, when two hydrogen nuclei (protons) fuse, a deuterium nucleus is produced
A positron and an electron neutrino are also produced as one of the protons converts into a neutron through beta-plus decay
In the centres of stars, four hydrogen nuclei
fuse to produce a helium nucleus
A huge amount of energy is released in the reaction
This provides a radiation pressure that prevents the star from collapsing under its gravity
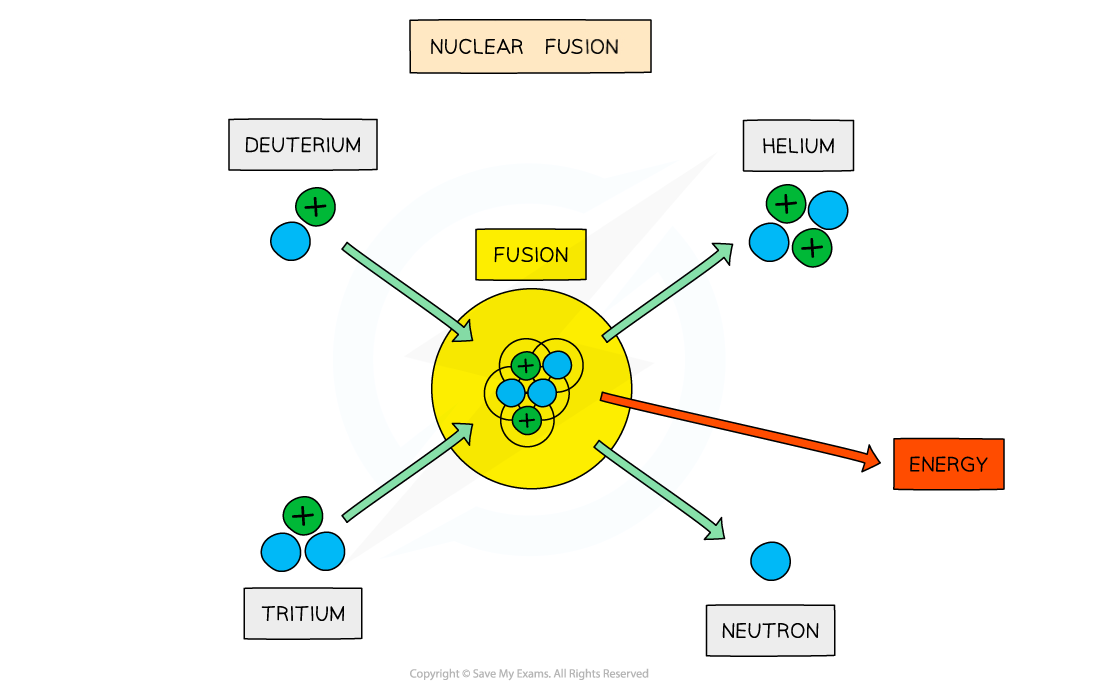
On Earth, research is focused on achieving the deuterium-tritium (D-T) reaction
This involves fusing a deuterium nucleus and a tritium nucleus together to produce a helium nucleus and a neutron
The total mass of the helium nucleus is less than the total mass of the individual nucleons
As a result, this reaction releases a large amount of energy per unit mass of fuel, which can be harnessed for power generation in a fusion reactor
Deuterium-tritium fusion
The role of the strong nuclear force in fusion
For two nuclei to fuse, both nuclei must have high kinetic energy
This is because
nuclei must overcome the repulsive Coulomb forces between protons
the strong nuclear force, which binds nucleons together, has a very short range
Therefore, nuclei must get very close together for the strong nuclear force to take effect
This means that, to achieve fusion, the nuclei must be
in an extremely hot and dense environment, e.g. the core of a star
accelerated to extremely high velocities, e.g. in a particle accelerator
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In the fusion process, the mass of the new, heavier nucleus is less than the mass of the constituent parts of the nuclei fused together, as some mass is converted into energy.
Not all of this energy is used as binding energy for the new, larger nucleus, so energy will be released from this reaction. The binding energy per nucleon afterwards is higher than at the start.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
