Scalar & Vector Quantities (DP IB Physics): Revision Note
Scalar & vector quantities
Scalars
Scalars are quantities that have magnitude only
For example, mass is a scalar quantity because it has magnitude but no direction
Vectors
Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction
For example, weight is a vector quantity because it is a force and has both magnitude and direction
Distance and displacement
Distance is a measure of how far an object has travelled, regardless of direction
Distance is the total length of the path taken
Distance, therefore, has a magnitude but no direction
So, distance is a scalar quantity
Displacement is a measure of how far it is between two points in space, including the direction
Displacement is the length and direction of a straight line drawn from the starting point to the finishing point
Displacement, therefore, has a magnitude and a direction
So, displacement is a vector quantity
What is the difference between distance and displacement?
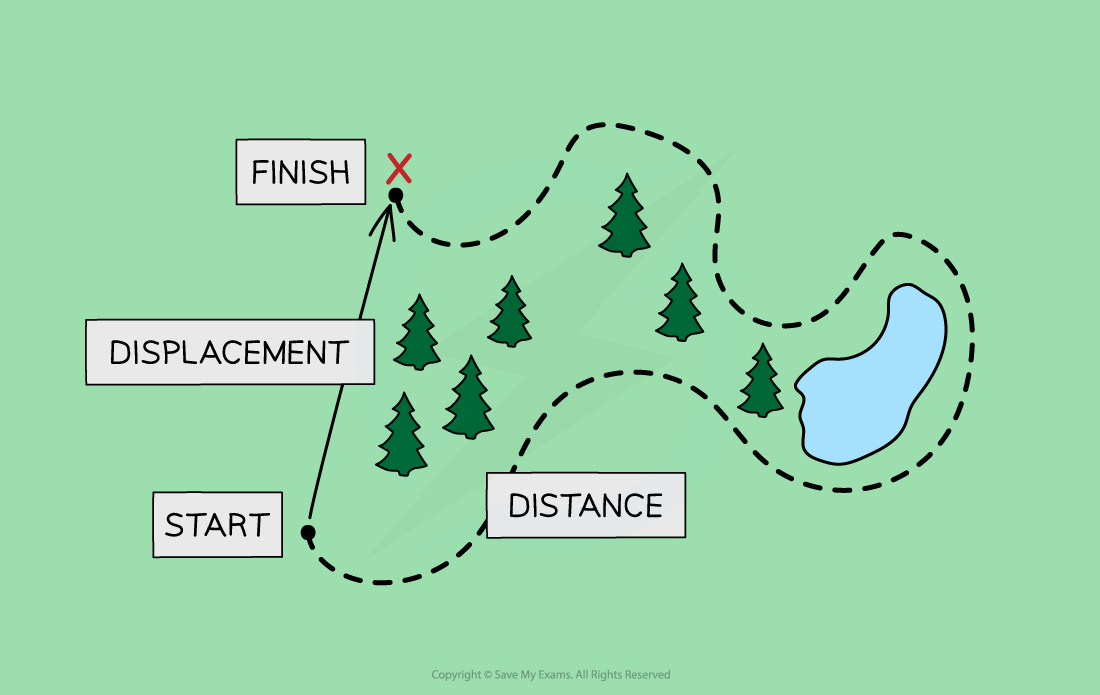
Displacement is a vector quantity, while distance is a scalar quantity
When a student travels to school, there will probably be a difference in the distance they travel and their displacement
The overall distance they travel includes the total length of all the roads, including any twists and turns
The overall displacement of the student would be a straight line between their home and school, regardless of any obstacles, such as buildings, lakes or motorways, along the way
Speed and velocity
Speed is a measure of the distance travelled by an object per unit time, regardless of the direction
The speed of an object describes how fast it is moving, but not the direction it is travelling in
Speed, therefore, has magnitude but no direction
So, speed is a scalar quantity
Velocity is a measure of the displacement of an object per unit time, including the direction
The velocity of an object describes how fast it is moving and the direction it is travelling in
An object can have a constant speed but a changing velocity if the object is changing direction
Velocity, therefore, has magnitude and direction
So, velocity is a vector quantity
Examples of scalars and vectors
Some common scalar and vector quantities are shown in the table below:
Table of scalars and vectors
Scalars | Vectors |
|---|---|
distance | displacement |
speed | velocity |
mass | acceleration |
time | force |
energy | momentum |
volume |
|
density |
|
pressure |
|
electric charge |
|
temperature |
|
Representing vectors
Vectors are represented by an arrow
The arrowhead indicates the direction of the vector
The length of the arrow represents the magnitude

The force vector F has both a direction and a magnitude
Component vectors are sometimes drawn with a dotted line and a subscript indicating horizontal or vertical
For example, Fx is the horizontal component and Fy is the vertical component of the force F
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Do you have trouble figuring out if a quantity is a vector or a scalar? Just think - can this quantity have a minus sign? For example, can you have negative energy? No. Can you have negative displacement? Yes!

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
