Growth (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
Reasons to grow
Businesses grow to achieve a range of key objectives
1. Economies of scale
Internal economies of scale
As a business grows, it can reduce its average costs
For example, it may be able to buy supplies in bulk or invest in more efficient machinery
External economies of scale
These are benefits that come from being part of a growing industry, such as better infrastructure or access to a skilled workforce
2. Increased market power
A larger business may have more control over customers and suppliers
It can influence prices or force suppliers to offer better terms, such as longer trade credit periods
3. Increased market share and brand recognition
Growth allows a firm to reach more customers and become better known
This can lead to higher sales and increased customer loyalty
Increased brand recognition can help further growth, as customers are familiar with and trust the brand
4. Increased profitability
Profitability is a measure of how efficiently a company generates profit relative to its revenue or investment
As a firm grows, it may be able to generate more revenue while controlling costs, boosting profitability
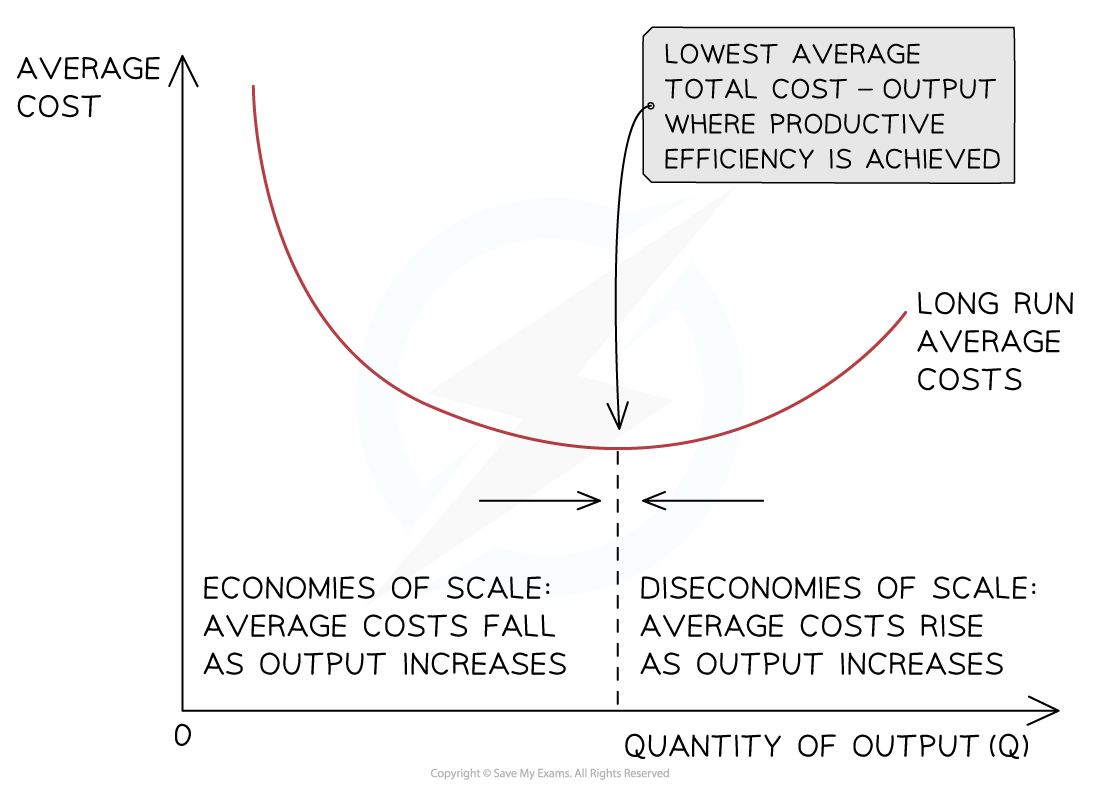
Explaining economies of scale
As a business grows, it can increase its scale of output, generating efficiencies that lower its average costs of production
These efficiencies are called economies of scale
Economies of scale help large firms to lower their costs of production beyond what small firms can achieve
As a firm continues increasing its scale of output, it will reach a point where its average costs (AC) will start to increase
The reasons for the increase in the average costs are called diseconomies of scale
Internal economies of scale occur as a result of the growth in the scale of production within the firm
Economies of scale
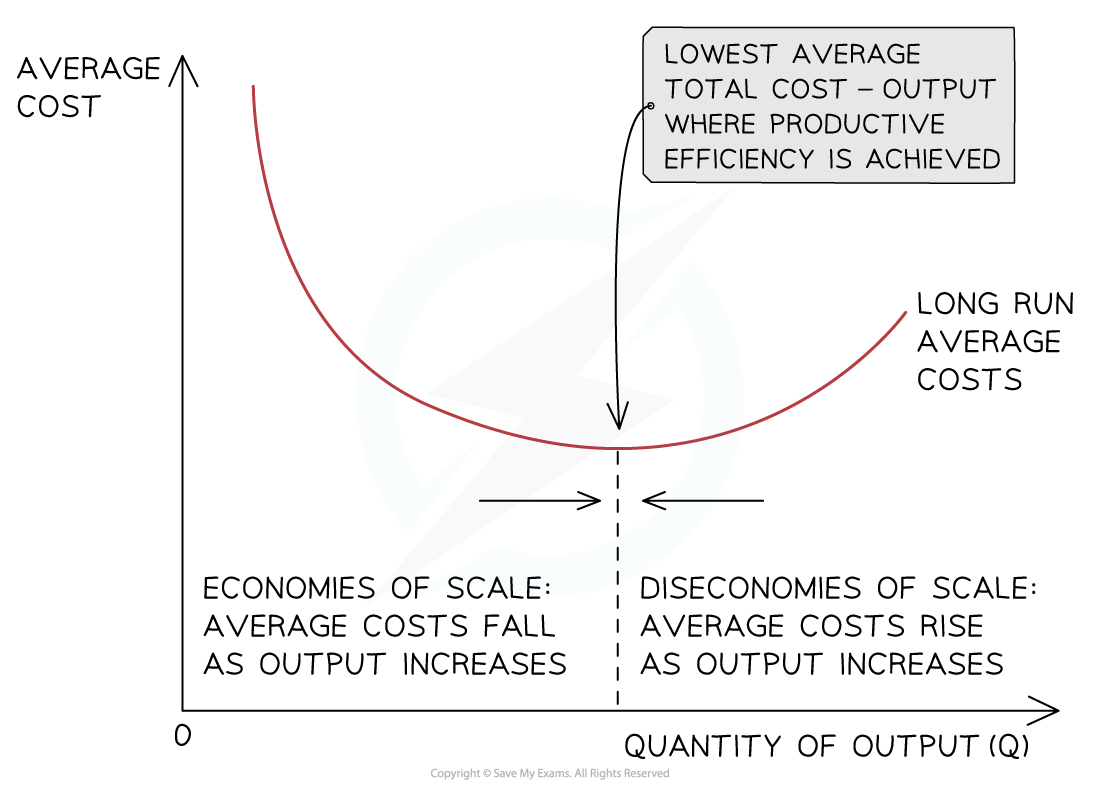
Diagram analysis
With relatively low levels of output, average costs are high
As the business increases its output, it begins to benefit from economies of scale, which lower the average cost per unit
At some level of output, a business will not be able to reduce costs any further — this point is called productive efficiency
Beyond this level of output, the average costs will begin to rise as a result of diseconomies of scale
Types of internal and external economies
Internal economies of scale
Internal economies of scale occur as a result of the growth in the scale of production within the business
The firm can benefit from lower average costs generated by factors that are inside the business
Types of internal economies of scale
Type | Explanation |
|---|---|
Financial economies |
|
Managerial economies |
|
Marketing economies |
|
Purchasing economies |
|
Technical economies |
|
Risk-bearing economies |
|
External economies of scale
External economies of scale occur when there is an increase in the size of the industry in which the firm operates
The firm benefits from lower average costs generated by factors outside of the business
Sources of external economies of scale
Source | Explanation |
|---|---|
Geographic cluster |
|
Transport links |
|
Skilled labour |
|
Favourable legislation |
|
Problems arising from growth
Rapid business growth may create challenges that can negatively impact a company's operations and financial performance
Three of these challenges are diseconomies of scale, internal communication issues and overtrading
1. Diseconomies of scale
This occurs when a company grows too large, making it difficult to manage and control its operations
It may face challenges in coordinating its various departments, managing its workforce or maintaining quality control
The cost per unit ends up increasing as a result of these inefficiencies
2. Internal communication
Rapid growth may strain communication channels or result in miscommunication, causing conflicting priorities and a lack of coordination
This may result in delays, errors and missed opportunities, as well as impact employee morale
3. Overtrading
This occurs when a company takes on more business than it can handle, leading to a strain on its resources or an inability to meet its financial obligations (lack of liquidity)
This may cause cash flow problems or decreased customer satisfaction
E.g. a company that expands too quickly may struggle to hire and train enough staff to handle increased demand, leading to a backlog of orders and dissatisfied customers

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
