Branding & Promotion (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
Types of promotion
Promotion is an important element of the marketing mix, as it plays a crucial role in generating customer awareness, interest and desire for a product/service
A business can communicate its value proposition to potential customers and differentiate itself from competitors
Promotion helps to build brand awareness and loyalty, which can lead to repeat purchases and referrals
The promotion element of the marketing mix includes a variety of promotional methods
Types of promotion
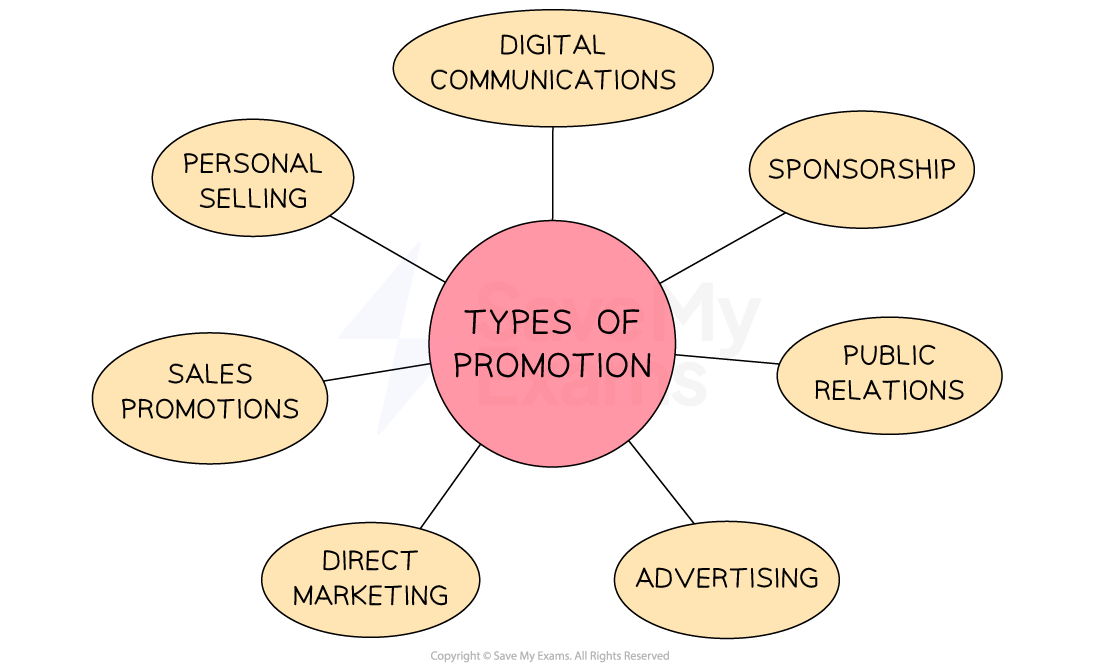
Each method has advantages and disadvantages associated with its use
Businesses must select the most appropriate methods for their product/service, target audience and budget
An assessment of promotional strategies
Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Advertising
|
|
|
Direct marketing
|
|
|
Sales promotions
|
|
|
Personal selling
|
|
|
Sponsorship
|
|
|
Public relations (PR)
|
|
|
Digital communications
|
|
|
Types of branding
Branding is the process of creating a unique and identifiable name, design, symbol or other feature that differentiates a product or company from its competitors
Branding is important to a business for a variety of reasons:
Branding establishes recognition and identity
Branding builds trust and credibility
Branding differentiates a business from its competitors
Branding creates an emotional connection with customers that helps to generate repeat purchases
Branding supports marketing and advertising efforts
Types of branding
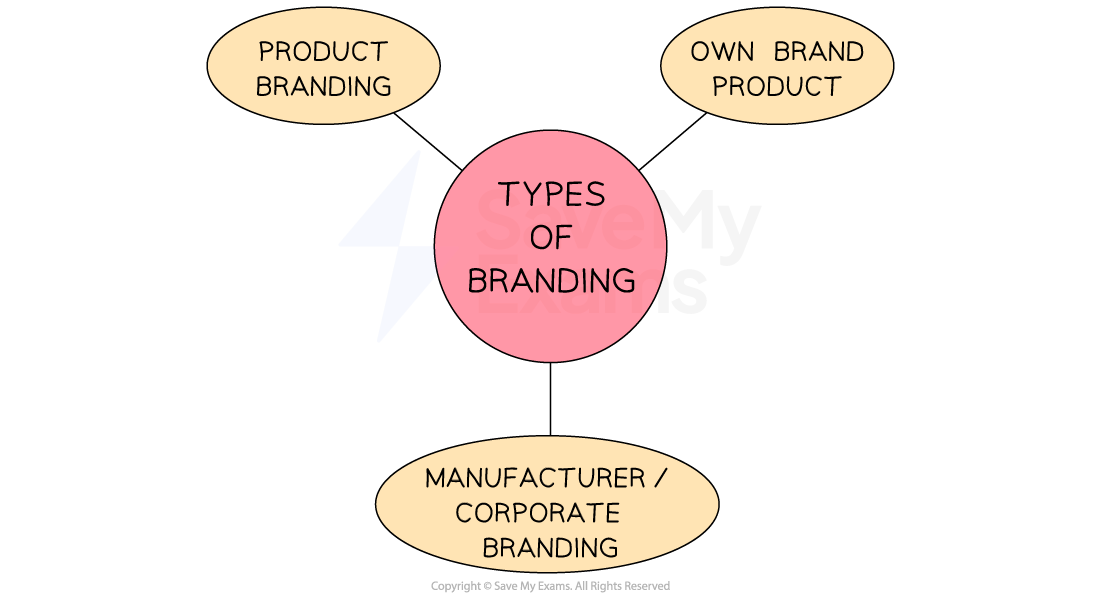
Manufacturer/corporate branding
This refers to the use of a company name or logo to promote all the products or services offered by the company
This type of branding is used by companies such as Nestlé, Nike and Apple
Advantages and disadvantages of corporate branding
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Product branding
This refers to the use of a unique name, design or symbol to promote a specific product
For example, KitKat, Coca-Cola and the McDonald's Big Mac
Advantages and disadvantages of product branding
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Own branding
Own-brand or private-label branding refers to the use of a retailer's name to promote a specific product or service
Own branding is often used by supermarkets, such as Asda chocolate, Tesco's "Finest" range and Sainsbury's "Basics" range
Advantages and disadvantages of own-brand products
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
The benefits of branding
Strong branding can provide several benefits to a business, including:
Added value
Strong branding can add value to a product by creating a perception of quality, reliability and trust
Ability to charge premium prices
Customers may be willing to pay more for a product that is associated with a well-established brand
They perceive products with strong branding to be of higher quality and therefore worth the extra cost
Reduced price elasticity of demand
Strong branding can also reduce the price elasticity of demand for a product (customers are less sensitive to price changes)
This is because customers who are loyal to a brand are more likely to continue purchasing the product even if the price increases
Ways to build a brand
Brands can be built using any one or a combination of the following methods:
By developing unique selling points (USPs)
Through advertising
Through sponsorship
Through the use of social media
Examples of brand building
Method | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
Unique selling points (USPs) |
|
|
Advertising |
|
|
Sponsorship |
|
|
Social media |
|
|
Changes in branding and promotion to reflect social trends
Businesses that respond quickly to changing social trends can better meet the needs of customers
Being able to quickly adapt branding and promotion strategies helps maximise communication opportunities with customers, which can develop brand loyalty and increase profits
Three current social trends businesses are aware of and adapting to are viral marketing, the use of social media and emotional branding
Viral marketing
This is a strategy in which businesses use online platforms to promote products by creating content at specific times, which can easily be shared and commented on
For example, during the Covid-19 pandemic, Coca-Cola and McDonald's ran campaigns that emphasised community, which aligned with the public's need for social support
Social media
As social media platforms evolve, businesses must also adapt their social media strategies to keep up with the latest trends
For example, Instagram has been a popular platform for businesses to promote products through influencer partnerships
More recently, many businesses have shifted focus to promoting their brands through short-form video content on platforms such as TikTok
Emotional branding
Emotional branding is a strategy in which companies build strong emotional connections with customers by appealing to their values, beliefs and emotions
For example, brands such as Patagonia and TOMS have built entire brand identities around a strong commitment to environmental and social causes, which resonates with customers who prioritise these values

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
