Molecular Matter (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0625 & 0972
Arrangement & motion of particles
All molecules and matter are in motion at room temperature
The motion and arrangement of particles must be known for each state of matter
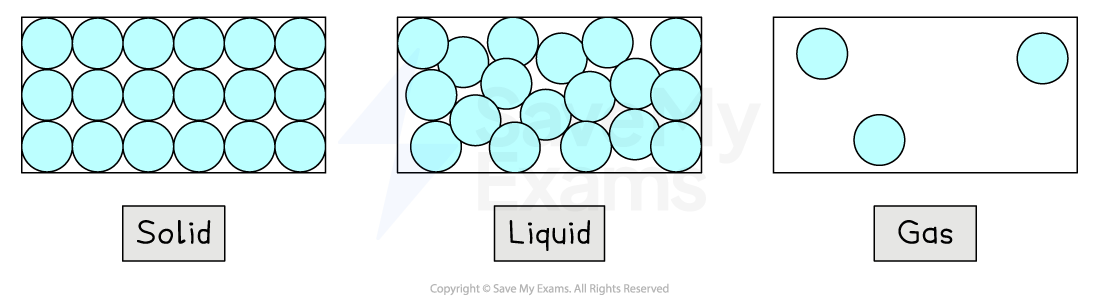
In a solid:
The molecules are very close together and arranged in a regular pattern
The molecules vibrate about fixed positions
In a liquid:
The molecules are still close together (no gaps) but are no longer arranged in a regular pattern
The molecules are able to slide past each other
In a gas:
The molecules are widely separated - about 10 times further apart in each direction
The molecules move about randomly at high speeds
Properties of states of matter
State | Solid | Liquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|---|
Density | High | Medium | Low |
Arrangement of particles | Regular pattern | Randomly arranged | Randomly arranged |
Movement of particles | Vibrate around a fixed position | Move around each other | Move quickly in all directions |
Energy of particles | Low energy | Greater energy | Highest energy |
The forces & distances between molecules
Extended tier only
Intermolecular forces and motion of particles
The forces between molecules and matter (or 'particles') affect the state of matter
This is because the magnitude of the forces affects the relative distances and motion of the particles
This affects the ability of the substance to
Change shape
Change volume
Flow
The word particles can refer to:
Atoms
Molecules
Ions
Electrons
Solids
The molecules in a solid are held in place by strong intermolecular forces
They only vibrate in position
The distance between them is fixed and is very small
This gives the solid its rigid shape and fixed volume
Liquids
The molecules in a liquid have enough energy to overcome the forces between them
They are still held close together
The volume of the liquid is the same as the volume of the solid
Molecules can move around (by sliding past each other)
This allows the liquid to change shape and flow
Gases
The molecules in a gas have more energy and move randomly at high speeds
The molecules have overcome the forces holding them close together
Because of the large spaces between the molecules
The gas can easily be compressed and is also able to expand
Gases flow freely
Worked Example
Two states of matter are described below. Identify each of the states of matter.
Substance 1
molecules are spaced very far apart
molecules move very quickly at random
molecules move in a straight line
Substance 2
molecules are quite closely packed together
molecules move about at random
molecules do not have fixed positions
Answer:
Substance 1
Step 1: Identify the distances between the molecules
The molecules are spaced far apart
This can only describe a gas
Step 2: Identify the motion of the molecules
The molecules move quickly, at random and in a straight line
This confirms that substance 1 is a gas
Substance 2
Step 1: Identify the distances between the molecules
The molecules are closely packed
This could describe either a solid or a liquid
Step 2: Identify the motion of the molecules
The molecules move at random and do not have fixed positions
This confirms that substance 2 is a liquid
Temperature & energy of particles
As the temperature of a gas increases, so does the average speed of particles in the gas
At higher temperatures, the particles have more kinetic energy
The amount of pressure that a gas exerts on its container is dependent on the temperature of the gas
This is because particles gain kinetic energy as their temperature increases
Therefore, there must be a temperature at which the particles are stationary
This is the lowest possible temperature, as particles cannot travel any slower than 0 m/s
The temperature at which all particles are stationary is called absolute zero
Absolute zero has a value of −273 °C

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
