The External Business Environment (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
Political and legal environment
The political environment
Government policy has had a significant indirect impact on the UK confectionery and biscuits markets over the last decade
Political influence | Explanation and impact |
|---|---|
Focus on reducing sugar consumption |
|
Decisions linked to Brexit |
|
The legal environment
Over the last decade, there has been a tightening of food labelling and consumer protection laws
Confectionery and biscuit businesses must now:
clearly display allergen information
comply with stricter food safety regulations
ensure marketing claims are accurate and not misleading
Confectionery and biscuits that can be reformulated to fall outside HFSS rules have gained a legal advantage
Examples include lower-sugar or higher-fibre biscuits,
Legal changes following Brexit have also increased regulatory complexity, as UK businesses must now comply with UK-specific rules rather than EU-wide systems
Impact on small businesses
Political and legal changes tend to have a greater impact on small businesses than on large multinationals.
For small confectionery and biscuit businesses:
Compliance costs are proportionally higher
Reformulating products is more expensive and risky
Legal advice and expertise are harder to afford
Brexit-related paperwork and rising compliance costs have been especially challenging for small firms that:
rely on imported ingredients
export small volumes to the EU
operate with tight profit margins
However, there are also opportunities for small businesses:
Premium and artisanal products are less reliant on price promotions
Ethical and transparent labelling can build trust
Small firms can adapt recipes and messaging more quickly than large firms
Economic environment
The confectionery market has been strongly influenced by changes in the UK economic environment, particularly since 2020
Key economic factors include high inflation, falling real incomes and rising production costs
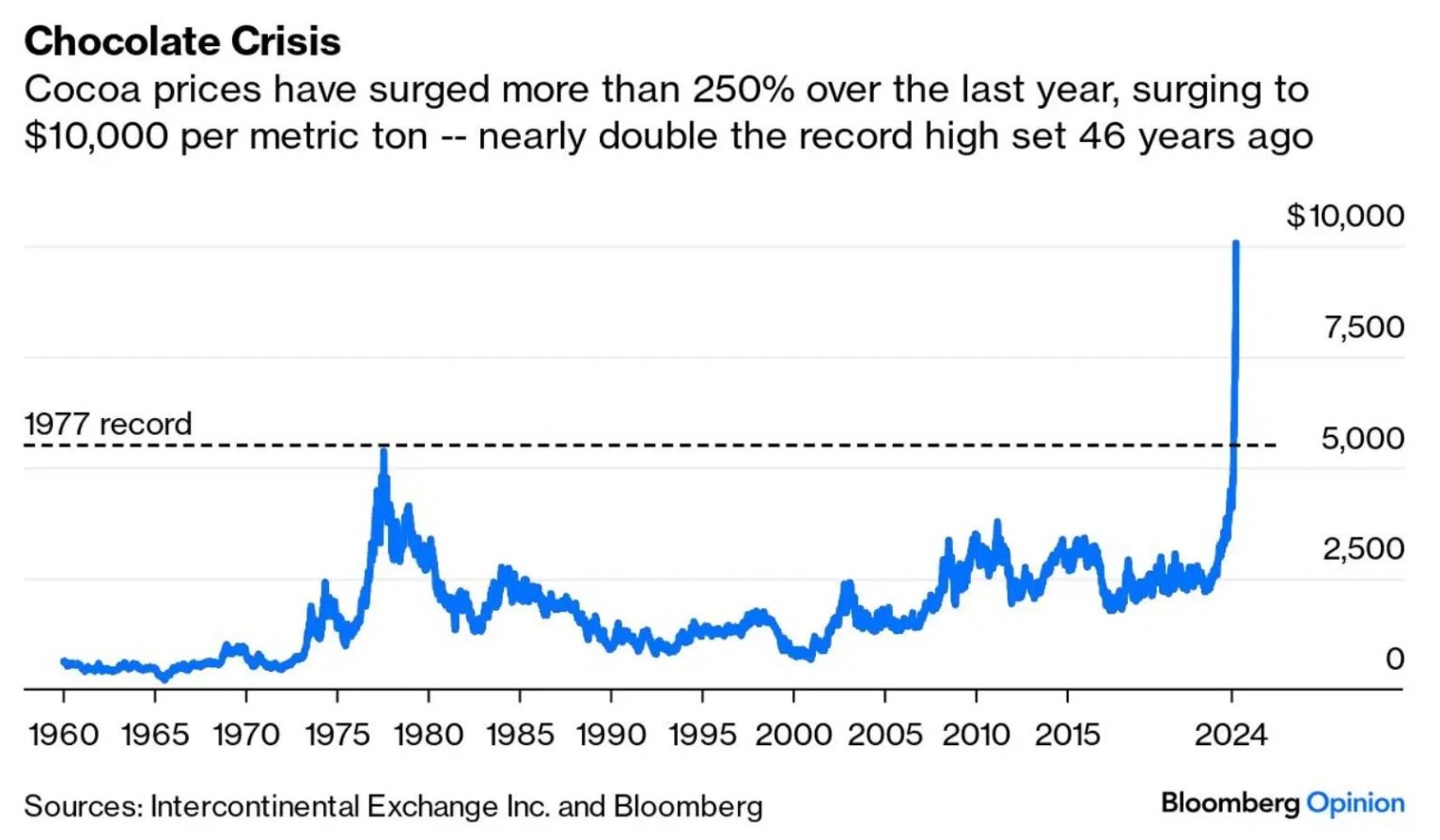
Inflation peaked in 2022–2023, increasing the cost of essential ingredients such as cocoa, sugar, milk and energy
Cocoa prices rose especially sharply due to poor harvests and supply shortages, pushing up production costs for chocolate manufacturers
Biscuits, which are often bought as part of regular household shopping, have been more directly affected by economic pressure
This has led to a greater focus on value for money, increased demand for own-label biscuits, and falling sales volumes, even where total spending has risen
Despite these pressures, demand for confectionery and biscuits has remained relatively resilient
Rather than stopping purchases altogether, consumers increasingly see them as affordable treats
Many have responded by
buying smaller pack sizes or multipacks
switching brands
waiting for promotions
reducing how often they buy
Premium biscuits have continued to grow, mainly among higher-income consumers who are less affected by rising living costs
Impact on small businesses
Economic changes tend to affect small confectionery and biscuit businesses more severely than large multinationals
Rising ingredient and energy costs are harder to absorb
They have less bargaining power with suppliers
Cash flow becomes more unpredictable during periods of economic instability
Unlike large firms, small businesses often cannot:
negotiate long-term fixed-price contracts
spread cost increases across a wide product range
rely on international sales to offset UK downturns
As a result, small businesses may be forced to:
increase prices more sharply
reduce product ranges
limit growth plans or investment
However, there are also opportunities for small businesses in difficult economic conditions
Some consumers reduce spending on eating out and choose premium treats at home instead
This can benefit artisan confectionery and biscuit producers
Small firms that clearly communicate quality, ethics or local production may continue to attract customers despite higher prices
Social, ethical and environmental environment
The social environment
Social changes over the last decade have had a strong influence on the UK confectionery market, particularly changes in consumer attitudes to health, lifestyle and consumption habits
Social trend | Explanation and impact |
|---|---|
Increased health awareness |
|
Confectionery as a treat or reward |
|
Changing lifestyles and working patterns |
|
Social media influence |
|
The ethical and environmental environment and the confectionery market
Ethical and environmental concerns have become increasingly important in the confectionery market, particularly around cocoa sourcing and labour practices
Over the last decade, awareness has grown of child labour, low farmer incomes and deforestation linked to cocoa production
As a result, consumers are more interested in chocolate that is ethically sourced, traceable and backed by clear sustainability commitments
Large brands have responded through ethical sub-brands and public sustainability pledges
However, challenger brands such as Tony’s Chocolonely have gained attention by making ethics central to their identity rather than an add-on

In the biscuit market, ethical and environmental concerns focus more on ingredients and packaging than global supply chains
Key issues include the use of palm oil, the sustainability of wheat and sugar production, and excessive packaging and food waste
Consumers are increasingly attracted to biscuits made with sustainably sourced ingredients and recyclable or minimal packaging
Across both markets, environmental pressure has increased costs, as businesses invest in recyclable packaging, improved energy efficiency and reduced food waste.
Impact on small businesses
Social, ethical and environmental changes create both challenges and opportunities for small confectionery and biscuit businesses
Ethical sourcing and sustainable packaging often involve higher costs
Meeting consumer expectations can be expensive and complex
Certification schemes (e.g. Fairtrade) can be costly and time-consuming
However, small businesses often benefit because:
Ethical and environmental values can be built into the brand from the start
Consumers may trust small, transparent businesses more
Differentiation through ethics can justify premium pricing
Small businesses that clearly communicate social and environmental values are often better placed to attract loyal customers, even if their products are more expensive
Technological environment
Advances in manufacturing and processing technology have allowed large confectionery and biscuit producers to automate production
This helps them reduce unit costs, maintain consistent quality, and launch new products more quickly
Large firms; competitive positions have strengthened, especially in mass market chocolate and biscuits
Developments in food science have supported product innovation
Examples include new flavours and textures, improved shelf life, and the creation of smaller or portion-controlled products
Digital technology has transformed marketing and consumer insight
Social media platforms such as TikTok, Instagram and YouTube are now key tools for product launches and brand building, particularly among younger consumers
Businesses increasingly use influencer marketing, short-form video and targeted online advertising, as well as sales data and social media trends, to identify changing tastes and refine products
E-commerce has grown alongside online grocery shopping
Brands now compete digitally as well as on shelves, and packaging must be suitable for delivery
Technology has also improved logistics, making it easier to manage stock, forecast demand and respond quickly to changes in consumer behaviour.
Impact on small businesses
Challenges for small businesses include:
high costs of investing in new machinery or automation
limited access to advanced food technology
difficulty matching the production efficiency of large firms
As a result, small businesses often have higher unit costs, making it harder to compete on price
However, technology also creates important opportunities for small businesses to
sell directly to consumers through websites and online marketplaces
market products cheaply through social media
build strong brand identities without large advertising budgets
Small firms can also use technology to:
manage orders and stock more efficiently
test new products in small batches
reach national or international customers without physical stores

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
