Efficiency (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 0625 & 0972
Did this video help you?
Efficiency of energy transfer
The efficiency of a system is a measure of the amount of useful and wasted energy in an energy transfer
Efficiency is defined as:
The ratio of the useful power or energy output from a system to its total power or energy input
If a system has high efficiency, this means most of the energy transferred is useful
If a system has low efficiency, this means most of the energy transferred is wasted
Calculating efficiency
Extended tier only
Efficiency is represented as a percentage and can be calculated using two equations
Efficiency in terms of energy:
Efficiency in terms of power:
In the production of electricity:
Energy is used to heat water to produce steam
The steam turns a turbine
The turbine turns a generator
The generator produces electricity
At each stage of this process, energy is dissipated to the surroundings
The overall efficiency of a typical thermal power station is approximately 30%
This means that 70% of the energy transferred from the power station to the National Grid is wasted energy
Sankey diagram of electricity production
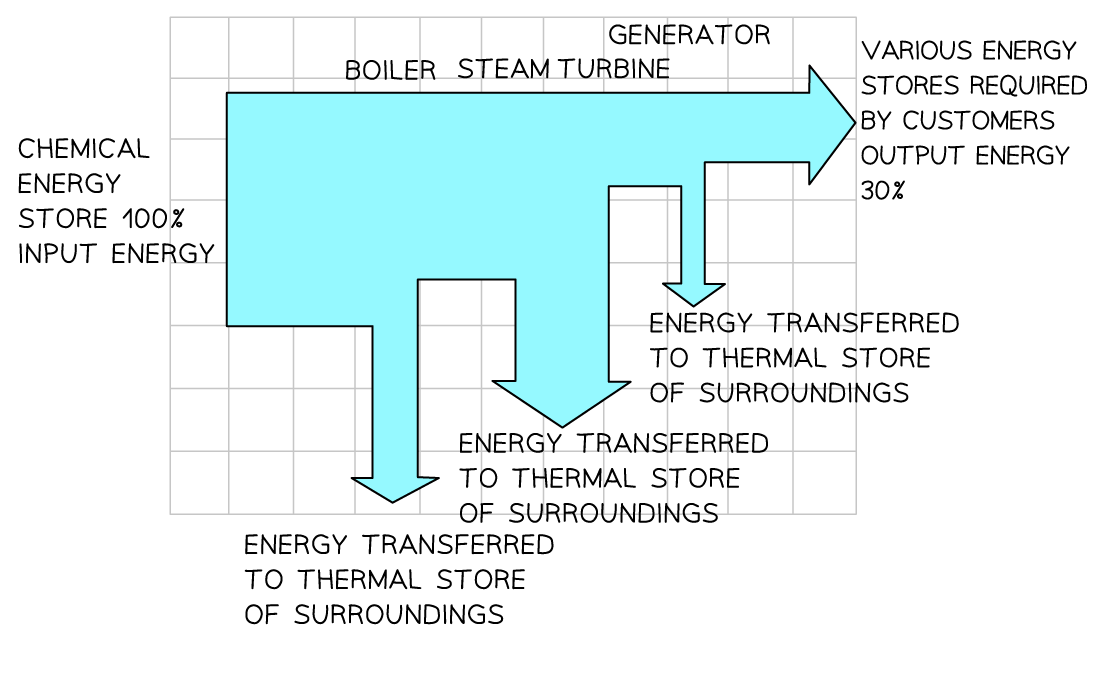
Sankey diagram showing the energy transfers involved in generating electricity in a gas-fired power station
Worked Example
An electric motor lifts a 7.2 kg load through a height of 5.0 m in 3 seconds. The efficiency of the motor is 35%.
Calculate the power supplied to the motor.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Mass of load,
= 7.2 kg
Change in height,
= 5.0 m
Acceleration of free fall,
= 9.8 m/s2
Time,
= 3 s
Efficiency = 35% or 0.35
Step 2: Calculate the power output of the motor
The power supplied by the motor is the work done, or energy transferred, to lift the load
is equal to the change in gravitational potential energy as the load is lifted
Therefore:
Step 3: Write down the efficiency equation in terms of power
Step 4: Rearrange to make power input the subject
Step 5: Substitute the values into the power input equation
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Efficiency can be given in a ratio (between 0 and 1) or percentage format (between 0 and 100 %)
If the question asks for efficiency as a ratio, give your answer as a fraction or decimal.
If the answer is required as a percentage, remember to multiply the ratio by 100 to convert it:
if the ratio = 0.25, percentage = 0.25 × 100 = 25 %
Remember that efficiency has no units
Did this video help you?

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
